Are you well aware of the symptoms and risks associated with periodontal disease? Have you recently been to a dentist for a check-up? If so, you may have recognized the need to take better care of your oral health. In this blog post, we’ll explore effective treatments for gum disease and some easy tips to help you prevent it in the first place. Read on as we provide an overview of how to deal with and maybe even avoid depression altogether.
Definition of Periodontal Disease
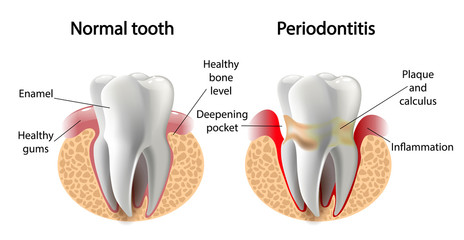
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection of the tissue and bones that support the teeth. This type of infection typically occurs due to poor oral hygiene habits or certain medical conditions such as diabetes. It has been linked to several systemic illnesses, including stroke, heart attack, and respiratory ailments. The most common symptoms include redness, swelling, pain in the gums (gingivitis), and bleeding when brushing or flossing. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss, receding gums, and even damage the underlying jawbone structure.
Overview of Causes & Symptoms
Periodontal disease is caused by bacteria that build up on the teeth and gums due to poor oral hygiene habits such as inadequate brushing, flossing, and rinsing of the mouth. Other causes include frequent snacking or eating sugary foods, smoking cigarettes, or using other tobacco products. These certain medications can cause dry mouth, ill-fitting dentures or braces, and systemic diseases such as diabetes.
Common symptoms of gum disease include swollen gums, which may appear puffy and red; persistent bad breath; tenderness of the gums when touched; receding gums (loose teeth); bleeding during brushing or flossing; loose teeth; and form pockets around the base of a tooth.
Treatments for Periodontal Disease
A. Non-Surgical Treatments
1. Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing) – This is a non-surgical procedure in which the dentist or hygienist will use special instruments to clean plaque and tartar buildup below the gum line and smooth the root surfaces of teeth to prevent bacteria from sticking to them. This treatment aims to reduce inflammation in the gums so that they can reattach themselves firmly to the teeth, preventing further damage.
2. Antibiotics – If an infection causes periodontal disease, antibiotics may be prescribed to kill off all harmful bacteria, reducing pain and swelling in the gums.
3. Oral Rinse/Mouthwash – Various over-the-counter oral rinses contain antibacterial agents that can help reduce plaque buildup and prevent further gum disease.
B. Surgical Treatments
1. Soft Tissue Grafts – This procedure replaces the missing tissue around a tooth, helping close gaps between teeth or covering exposed root surfaces, which could result in periodontal pocketing (pockets of infection).
2. Bone Grafts – A bone graft is used to replace damaged bone as a result of periodontal disease or trauma. The bone graft helps to support existing teeth and also facilitates the placement of dental implants.
3. Flap Surgery (Pocket Reduction Procedure) – This procedure is used to reduce the depth of the gum pockets formed due to periodontal disease and help eliminate the bacteria inside them. This surgery aims to help restore the area to health, promoting better plaque control and preventing further infection or damage.
Prevention Tips for Gum Disease
A. Regular Teeth Cleanings and Checkups with a Dentist or Hygienist – It is important to visit your dentist or hygienist at least twice a year for professional teeth cleaning and examination to identify any issues early on before they become more serious problems.
B. Good Oral Hygiene Habits
Brushing Twice Daily – Brushing your teeth twice a day with an ADA-approved soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste helps to remove plaque buildup and prevent cavities, gingivitis, and periodontal disease.
Flossing Regularly – Flossing should be done at least once a day to remove food particles that have become stuck between teeth which can lead to bacteria growth.
Using an Antiseptic Mouthwash – An antiseptic mouthwash can help kill off any remaining bacteria on the teeth, reducing the risk of periodontal disease from occurring.
C. Avoid Tobacco Products – Smoking cigarettes or using other tobacco products can increase your risk of developing gum disease, so it is important to avoid them.
D. Eat a Healthy Diet and Limit Sugary Snacks & Drinks – Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins helps keep teeth healthy and strong. Limiting sugary snacks and drinks (especially soda) will also help reduce the risk of cavities and gum disease.
E. Monitor Blood Sugar if Diabetic – Those with diabetes should closely monitor their blood sugar levels to prevent or delay the onset of periodontal diseases, which may be caused by complications associated with diabetes.
F. Wear a Nightguard to Prevent Teeth Grinding (Bruxism) – Wearing a nightguard while sleeping can help to protect teeth from grinding and clenching, which can lead to receding gums and periodontal disease.
Conclusion
With the right commitment to prevention and treatment regimes, people with gum disease can regain control of their oral health. And if it is too late to do DIY interventions, visiting a dentist in Monterey is recommended, as they can swiftly halt the progress of gum disease before serious damage irreversibly occurs. A quick dental checkup near you could detect the early signs of periodontal ailments and put in place preventive or curative measures much quicker than would be accomplished by self-care alone.
It may seem like a simple solution that removes the need for extensive surgery, but scheduling an appointment with the best dentist in Monterey may be more important for averting severe gum complications than is often perceived. Ultimately, individually designed preventive treatments remain vital after professional treatment to ensure sustained oral health improvements and maintain gum health over time.

