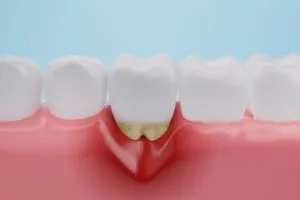
Symptoms and Causes of Gingival Recession also knows as Receding Gums
Gingival recession, also known as receding gums, is a common dental condition in which the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away or pulls back, exposing more of the tooth and its root. This can lead to sensitivity and discomfort.
Various Symptoms of Receding Gums
The most obvious symptom of receding gums is the visible exposure of the tooth root, which can cause the tooth to appear longer than normal. Other symptoms may include:
- Tooth sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures
- Discomfort or pain while eating or drinking
- A visible notch at the gum line
- Loose teeth or change in bite
- Pus between teeth and gums
- Bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to see your dentist as soon as possible to determine the underlying cause of your receding gums and begin treatment to prevent further damage.
Causes of Receding Gums
There are several potential causes of receding gums, including:
- Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to the buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth and gum line, which can irritate and inflame the gums, leading to recession.
- Gum disease: Gingivitis and periodontitis are gum diseases caused by bacterial infections that attack the gums and can lead to inflammation, gum recession, and even tooth loss if left untreated.
- Genetic predisposition: Some people may be more prone to receding gums due to genetic factors.
- Aggressive brushing: Brushing your teeth too hard or using a toothbrush with hard bristles can cause the enamel to wear away and the gums to recede.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can increase the risk of gum disease and gingival recession.
- Tobacco use: Smoking or using tobacco products can cause gum disease and lead to receding gums.
- Teeth grinding: Clenching or grinding your teeth can put excessive pressure on the gums, leading to recession.
Treatment for Receding Gums
The treatment for receding gums depends on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. Here are some common treatment options:
- Scaling and root planing: This deep cleaning treatment removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line and smooths the tooth root to prevent further buildup.
- Gum grafting: This surgical procedure involves taking tissue from another part of the mouth and attaching it to the affected area to cover the exposed tooth root and promote gum tissue regeneration.
- Antibiotics: If gum disease is the underlying cause of the recession, antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce the bacterial infection and promote healing.
- Lifestyle changes: Improving oral hygiene habits, quitting smoking, and reducing teeth grinding can help prevent and treat receding gums.
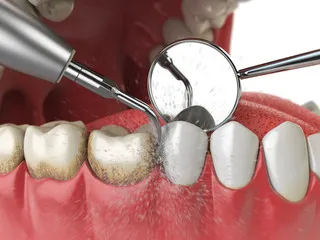
Preventing Receding Gums
Prevention starts with good oral hygiene habits. Here are some tips to keep your gums healthy and prevent gingival recession:
- Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss at least once a day to remove plaque and food particles from between teeth and along the gum line.
- Use an antimicrobial mouthwash to kill bacteria and freshen breath.
- Eat a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and calcium to support strong teeth and bones.
- Quit smoking or using tobacco products.
- Visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups to catch and treat gum disease and other dental problems early.
In conclusion, it can be a painful and unsightly dental condition, but with proper treatment and prevention, it can be managed effectively.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of receding gums, don’t wait to seek treatment. Contact your dentist today to schedule an appointment and discuss your options for preventing and treating gingival recession. With proper care and attention, you can keep your gums healthy and prevent further damage to your teeth and overall oral health.

